|
|
|
Wind parks constitute a concentrated way of exploiting wind energy affected to a considerable extend by wake effects. As a consequence, wind turbines operating in clusters will have reduced power output and lifetime.
 To investigate the impact of wake effects to the design and
performance of wind parks
To investigate the impact of wake effects to the design and
performance of wind parks
 To develop methods for better designing wind parks
To develop methods for better designing wind parks
A multi-level research activity has been conducted along the following guidelines:
 Simulation of the flow characteristics downstream the rotor
disk by means of advanced numerical models
Simulation of the flow characteristics downstream the rotor
disk by means of advanced numerical models
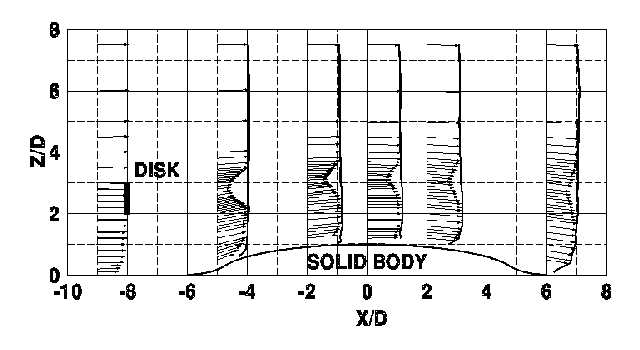
Near-wake region: A Navier-Stokes solver using the k-å turbulence model gives the velocity field and the turbulence characteristics of the flow over the mixing region of the wake. Input to this are the results of the rotor region.
Far-wake region: A multi-parametric far-wake model based on similarity assumptions is filled so as to get the inflow information further downstream.
 Investigation of the wake interaction among two or several
overlapping wakes
Investigation of the wake interaction among two or several
overlapping wakes
 Development and evaluation of an improved modular wind park
performance analysis engineering tool for flat terrains
Development and evaluation of an improved modular wind park
performance analysis engineering tool for flat terrains
 Investigation of the terrain effects to the performance of
wind parks
Investigation of the terrain effects to the performance of
wind parks
 Development of a method for the aerodynamically optimal design
of wind parks
Development of a method for the aerodynamically optimal design
of wind parks
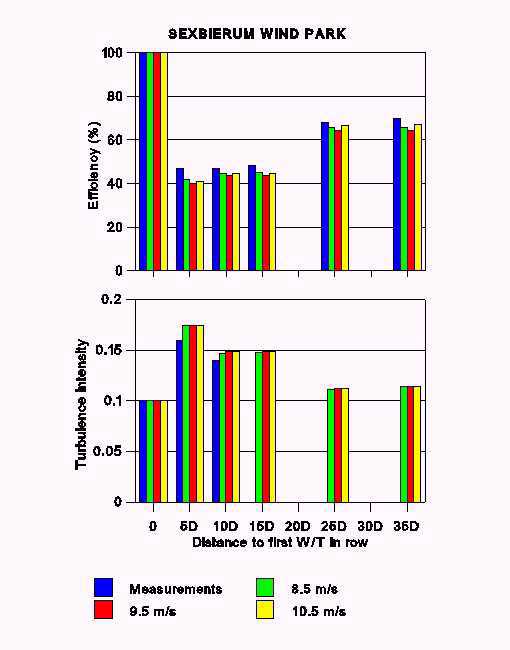
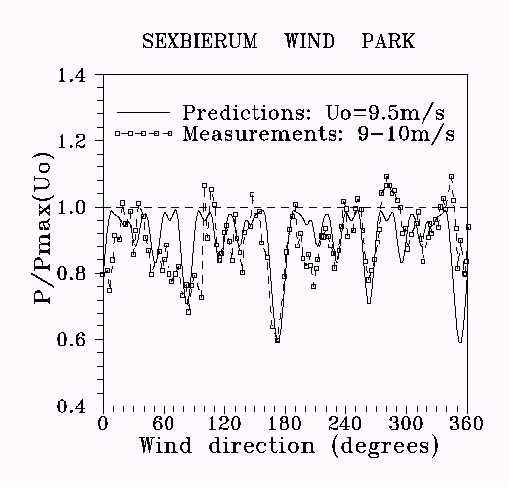
WINPPAN : WINd Park Performance Analysis code
It calculates the annual energy output, the individual machine output and the turbulence intensity to every wind turbine of a wind park with respect to the wind rose of the site.
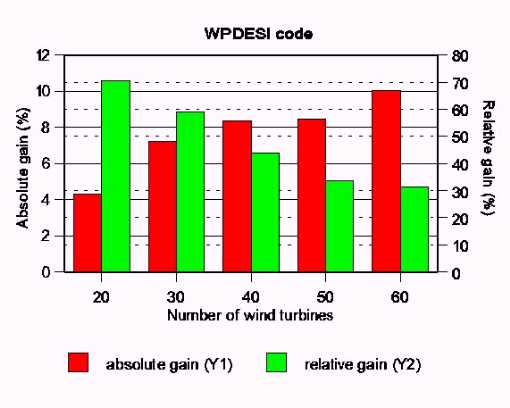
WPDESI : Wind Park DESIgn code
It provides the optimal lay-out of a wind park installed in a specific site for producing maximum annual energy.
|
|
|
|
|
|